| Arck PC et al. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
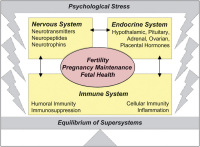
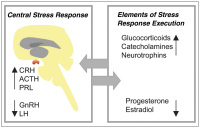
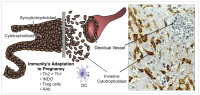
Current Insights and Future Perspectives on Neuro-Endocrine-Immune Circuity Challenging Pregnancy Maintenance and Fetal Health
Journal für Reproduktionsmedizin und Endokrinologie - Journal of Reproductive Medicine and Endocrinology 2006; 3 (2): 98-102 Volltext (PDF) Summary Abbildungen
|
||||||||||||||||||||||

Verlag für Medizin und Wirtschaft |
|
||||||||
|
Abbildungen und Graphiken
|
|||||||||
| copyright © 2000–2025 Krause & Pachernegg GmbH | Sitemap | Datenschutz | Impressum | |||||||||
|
|||||||||