Köppel H, Schöllnast R, Vidalli S Specific dihydropyridines may affect gating properties of certain subsets of adenosin-triphosphate-dependent K-channels in myocardial tissue and hence modulate its response to ischaemia Journal of Clinical and Basic Cardiology 2000; 3 (2): 133-134 PDF Summary Overview
| ||||
Figure/Graphic 1: Kalium - Ischämie Potassium recordings on the surface of an isolated guinea pig papillary muscle in NT-solution. Ischaemic episodes are indicated with time bars. The preparation is stimulated at a frequency of 1 Hz. Surface recordings show the accumulation of potassium during simulated ischaemia with a subsequent decrease of surface potassium (Ks) upon reperfusion. In the presence of nisoldipine potassium rises to a much lesser extent than in the presence of the drug. |
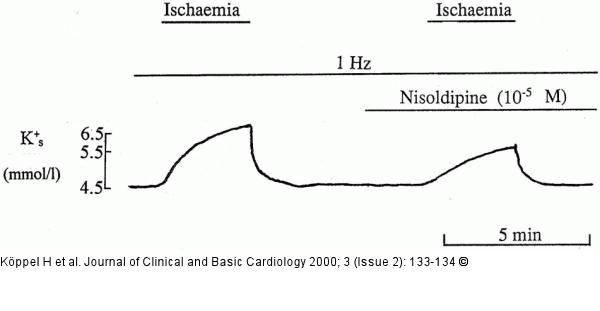
Figure/Graphic 1: Kalium - Ischämie
Potassium recordings on the surface of an isolated guinea pig papillary muscle in NT-solution. Ischaemic episodes are indicated with time bars. The preparation is stimulated at a frequency of 1 Hz. Surface recordings show the accumulation of potassium during simulated ischaemia with a subsequent decrease of surface potassium (Ks) upon reperfusion. In the presence of nisoldipine potassium rises to a much lesser extent than in the presence of the drug. |


