Carluccio E, Bentivoglio M, Biagioli P, Corea L, Prosciutti L, Tommasi S Relation between Doppler transmitral flow and wall motion abnormalities during dipyridamole echocardiography in coronary artery disease Journal of Clinical and Basic Cardiology 2000; 3 (1): 47-51 PDF Summary Overview
| ||||||
Figure/Graphic 1: Koronare Herzkrankheit - Dipyridamol-Streßechokardiographie Changes in Doppler indices during dipyridamole stress echocardiography. In group A (top panel) the reduction in E/A ratio was mainly due to a significant increase in peak A velocity at the end of dipyridamole infusion. In group B (bottom panel) the increased E/A ratio was due to a significant increase in peak E velocity and only a slight increase in peak A velocity. |
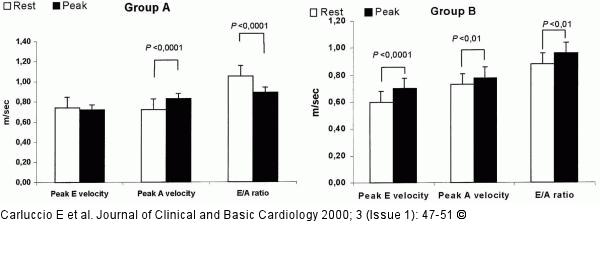
Figure/Graphic 1: Koronare Herzkrankheit - Dipyridamol-Streßechokardiographie
Changes in Doppler indices during dipyridamole stress echocardiography. In group A (top panel) the reduction in E/A ratio was mainly due to a significant increase in peak A velocity at the end of dipyridamole infusion. In group B (bottom panel) the increased E/A ratio was due to a significant increase in peak E velocity and only a slight increase in peak A velocity. |



