| Pinter MM | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Funktionelle elektrische Stimulation bei Schwäche der Vorfußhebung // Functional electrical Stimulation and drop foot Journal für Neurologie, Neurochirurgie und Psychiatrie 2016; 17 (3): 84-88 Volltext (PDF) Summary Praxisrelevanz Abbildungen
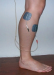
Keywords: funktionelle elektrische Stimulation, Neurorehabilitation, Upper-Motor-Neuron-Erkrankung, Vorfußheberschwäche, drop foot, functional electrical stimulation, upper motor neuron disease Drop foot is a common problem following neurological conditions such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, brain injury and incomplete spinal cord injury, consisting in the inability to lift the foot in the swing phase of the gait cycle. Since dropped foot is frequently associated with spasticity and more complex movement problems affecting the whole person, it can result in tripping and falling. Functional electrical Stimulation (FES) devices are designed to address this problem. The peroneal nerve is stimulated using surface electrodes at its most superficial position in its course, where it passes over the head of the fibula bone. The peroneal nerve stimulation induces activity in the tibialis anterior and peroneous longus muscles, causing dorsiflexion and eversion of the foot. The stimulation is synchronised to the gait using a pressure sensitive heel switch. When weight is taken from the switch, stimulation is given. FES results in an economisation of gait and an improvement of walking speed and walking distance. Recently, an implantable 4-channel drop foot stimulator with independent electrode adjustment resulting in a more specific stimulation showed an improvement of walking speed and a restoration of gait in patients with stroke. The therapeutic effect might be improved compared with surface stimulation.
Kurzfassung: Die Schwäche der Vorfußhebung
ist ein weit verbreitetes Problem bei neurologischen
Erkrankungen wie Schlaganfall, Multiple
Sklerose, Schädelhirntrauma und inkomplettem
Querschnittsyndrom und führt zu einer insuffizienten
Hebung des Vorfußes in der Schwungphase
des Gangzyklus. Vielfach ist die Schwäche der
Vorfußhebung assoziert mit Spastizität und komplexeren
motorischen Problemen, dies führt zu
gehäuftem Stolpern und Stürzen. |

Verlag für Medizin und Wirtschaft |
|
||||||||
|
Summary
|
|||||||||
| copyright © 2000–2025 Krause & Pachernegg GmbH | Sitemap | Datenschutz | Impressum | |||||||||
|
|||||||||