| Pfabe FP | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Der Glomus caroticum-Tumor: eine diagnostische und therapeutische Herausforderung // The Carotid-Glomustumor: a diagnostic and therapeutical Challenge Zeitschrift für Gefäßmedizin 2018; 15 (3): 6-10 Volltext (PDF) Summary Praxisrelevanz Abbildungen
Keywords: Diagnostik, Glomus-Caroticum-Tumor, Malignität, Paragangliom, Shamblin-Klassifikation, carotid body-tumor, diagnostic workup, malignancy, paragangliomas, Shamblin classification The rarely malignant carotid-glomustumor is classified as semimalignant due to its progressive growth. Affected patients often have hypoxemia of various origins. Diagnosis is usually random in asymptomatic patients, while tumor related symptoms are typically but nonspecific. CT and MRI allow a precise description of tumor size, invasiveness of growth and infiltration of surrounding tissue. The angiography is used for operative planning and allows preoperative embolization of the tumor. The treatment of choice is surgical extirpation. As the tumor size increases, the risk of complications increases. An alternative therapy of inoperable tumors is radiation.
Kurzfassung: Der selten maligne Karotis-Glomustumor
wird aufgrund seines progredienten
Wachstums als semimaligne eingestuft. Betroffene
Patienten weisen häufig eine Hypoxämie
unterschiedlicher Genese auf. Die Diagnosestellung
erfolgt bei asymptomatischen Patienten
in der Regel zufällig, während tumorbezogene
Symptome typisch, aber unspezifisch sind.
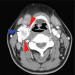
CT und MRT erlauben eine exakte Beurteilung
der Tumorgröße, der Invasivität des Wachstums
und der Infiltration des umgebenden Gewebes.
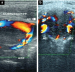
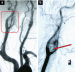
Die Angiographie dient der operativen Planung
und erlaubt präoperativ eine Embolisation des
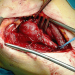
Tumors. Therapie der Wahl ist die chirurgische
Exstirpation. Mit zunehmender Tumorgröße
steigt das Komplikationsrisiko. Inoperable Tumoren
können alternativ bestrahlt werden. |

Verlag für Medizin und Wirtschaft |
|
||||||||
|
Summary
|
|||||||||
| copyright © 2000–2025 Krause & Pachernegg GmbH | Sitemap | Datenschutz | Impressum | |||||||||
|
|||||||||