| Rossmann T et al. | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Interdisziplinäres Management kindlicher Schädel-Hirn-Traumata // Multidisciplinary management of pediatric traumatic brain injury Journal für Neurologie, Neurochirurgie und Psychiatrie 2019; 20 (2): 64-70 Volltext (PDF) Summary Praxisrelevanz Abbildungen
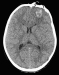
Keywords: Intensivmedizin, Neurochirurgie, Pädiatrie, Schädel-Hirn-Trauma, SHT, intensive care, Management, pediatric, traumatic brain injury Traumatic brain injury is one of the leading causes of death and permanent disability in pediatric patients. The adequate treatment approach includes surgical management of intracranial pathologies and multidisciplinary postoperative care with the aim to prevent secondary injuries, potentially causing neurocognitive deficits. Pediatric intensive care focuses on preventing posttraumatic brain edema and systemic complications. Neurosurgical operative interventions mainly include the implantation of devices to measure intracranial pressure and for cerebrospinal fluid drainage. Craniotomies are performed in cases of subdural or epidural hematoma, or penetrating head injuries with intracerebral lesions. Decompressive craniectomy may be performed for elevated intracranial pressure refractory to medical treatment. Close multidisciplinary cooperation is of utmost importance to master the challenges in traumatic brain injury. Standardized evidence based treatment protocols have to be quickly adapted to individual patients to achieve satisfactory outcomes. This requires joint efforts by neurosurgery, intensive care, pediatrics, neurology, occupational therapy, physical therapy and nursing staff as well as the involvement of parents if possible. The following pages outline a multidisciplinary treatment approach in a pediatric trauma center.
Kurzfassung: Das Schädel-Hirn-Trauma (SHT) ist eine der häufigsten Ursachen für Tod oder
bleibende Schäden im Kindesalter. Ziel der interdisziplinären Behandlung sind die operative
Sanierung intrakranieller Pathologien, die Anwendung
lebenserhaltender Maßnahmen sowie das Minimieren von sekundären Folgeschäden, insbesondere neurokognitiver Defizite. Die Kinderintensivmedizin leistet ihren Beitrag vor allem durch das Management des posttraumatischen Hirnödems und begleitender systemischer Komplikationen. Neurochirurgische
Interventionen betreffen meist die Anlage von
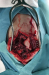
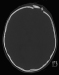
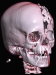
Hirndrucksonden, liquorableitender Systeme sowie Kraniotomien bei jenen Pathologien, die dies erfordern, etwa epidurale und subdurale Hämatome, penetrierende Verletzungen mit intrazerebralen Läsionen, oder die dekompressive Kraniektomie bei therapierefraktärem erhöhtem Hirndruck (ICP). |

Verlag für Medizin und Wirtschaft |
|
||||||||
|
Summary
|
|||||||||
| copyright © 2000–2025 Krause & Pachernegg GmbH | Sitemap | Datenschutz | Impressum | |||||||||
|
|||||||||