| Sáez Y et al. | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Lipoprotein (a) in a Sample of Children from the Province of Biscay Journal of Clinical and Basic Cardiology 2003; 6 (1-4): 53-54 PDF Summary Figures
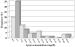
Keywords: Cholesterin, Kardiologie, Kind, Lipoprotein-a, Spanien, cardiology, child, cholesterol, Lipoprotein-a, Spain Atherosclerosis is a process that is initiated in the earlier stages of life. Moreover, Lipoprotein (a) [Lp(a)] has taken the form of an independent risk factor. All this justifies the study of Lp(a) in children. The Lp(a) plasma levels were determined in 115 children (51 girls and 64 boys) with ages ranging from 6 to 7 years. These children came from an epidemiological study on the prevalence of hypercholesterolaemia in children in the province of Biscay. ELISA was used to determine the Lp(a) concentration in each of the children and, at the same time, a lipid study was also carried out on them (total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, Apolipoprotein B and Apolipoprotein A1). The average Lp(a) concentrations were 11.51 ± 16.97 mg/dl for the boys and 13.87 ± 14.72 mg/dl for the girls. In the case of the boys, 10.9 % were shown to have Lp(a) concentrations of more than 30 mg/dl. In the case of the girls, 11.4 % were shown to have Lp(a) concentrations of more than 30 mg/dl. The boys had lower Lp(a) average values and prevalences that were > 30 mg/dl than the girls ones, although they were not statistically significant. We did not find any relationship between the high Lp(a) concentrations and the various lipid parameters studied. |

Verlag für Medizin und Wirtschaft |
|
||||||||
|
Summary
|
|||||||||
| copyright © 2000–2025 Krause & Pachernegg GmbH | Sitemap | Datenschutz | Impressum | |||||||||
|
|||||||||