Szili-Török T, Gingl Z, Halmai L, Kardos A, Rudas L Windowed FFT - a time-variant spectral analysis: applicability during the head-up tilt test Journal of Clinical and Basic Cardiology 1999; 2 (2): 241-244 PDF Summary Overview
| ||||||
Figure/Graphic 2A-D: Kipptisch Typical tilt-induced responses of a tilt-positive patient. Panel A. The RR interval tachogram. The tilting, indicated by a vertical line is reflected by an immediate HR acceleration. The sudden-onset bradycardia after 800 s of the recording coincides with the syncopal episode. Panel B. The systolic BP trend curve reveals transient stabilisation post-tilting, followed by a marked hypotension, eventually leading syncope. Panels C and D. Variations in HR (C) and systolic BP (D) with time, as assessed by windowed FFT in the same arrangement as in Figure 1. The upright tilt manoeuvre is paralleled by elevations in the LFHRV and TFHRV powers. The duration of the elevations in these frequency ranges is prolonged, however, relative to the normal, and they are interrupted by further peakings. The subsequent decreases in the spectral components precede the syncopal episode. |
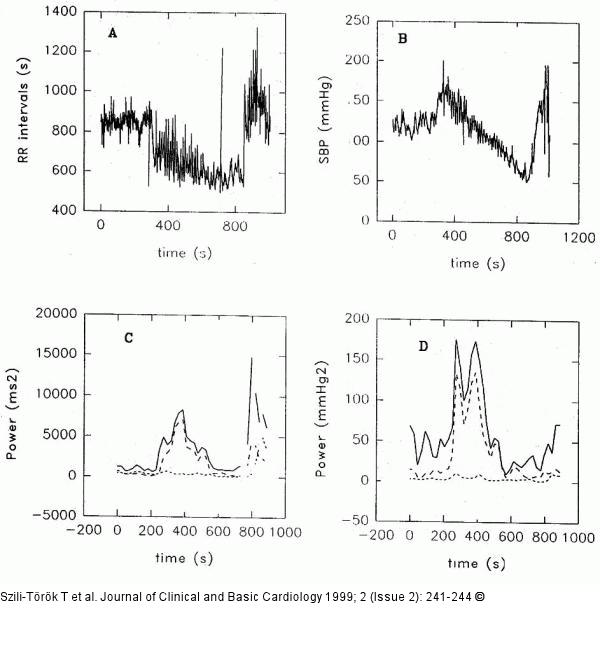
Figure/Graphic 2A-D: Kipptisch
Typical tilt-induced responses of a tilt-positive patient. Panel A. The RR interval tachogram. The tilting, indicated by a vertical line is reflected by an immediate HR acceleration. The sudden-onset bradycardia after 800 s of the recording coincides with the syncopal episode. Panel B. The systolic BP trend curve reveals transient stabilisation post-tilting, followed by a marked hypotension, eventually leading syncope. Panels C and D. Variations in HR (C) and systolic BP (D) with time, as assessed by windowed FFT in the same arrangement as in Figure 1. The upright tilt manoeuvre is paralleled by elevations in the LFHRV and TFHRV powers. The duration of the elevations in these frequency ranges is prolonged, however, relative to the normal, and they are interrupted by further peakings. The subsequent decreases in the spectral components precede the syncopal episode. |