Wendlová J Muscular Dysbalance in Mm. Coxae Area and its Clinical Significance for Patients with Osteoporosis Journal für Mineralstoffwechsel & Muskuloskelettale Erkrankungen 2002; 9 (2): 7-12 Volltext (PDF) Summary Übersicht
| ||||||||||
Abbildung 2: Hüftmuskulatur Biomechanical scheme of force resolution in muscular balance: Q = the force vector, which simulates the action of the weight of the upper part of the body on articulatio and mm. coxae. Force Q resolutes into force F1 acting on flexors and F2 acting on extensors. F1 = the force vector transfered into flexors. F2 = the force vector transfered into extensors. |
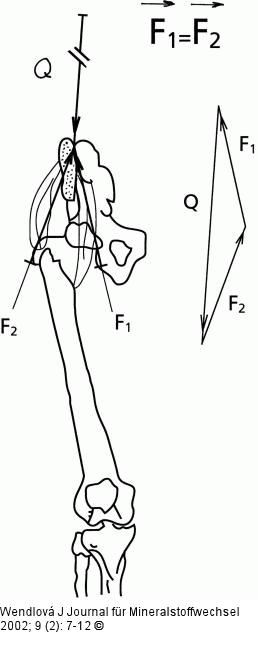
Abbildung 2: Hüftmuskulatur
Biomechanical scheme of force resolution in muscular balance: Q = the force vector, which simulates the action of the weight of the upper part of the body on articulatio and mm. coxae. Force Q resolutes into force F1 acting on flexors and F2 acting on extensors. F1 = the force vector transfered into flexors. F2 = the force vector transfered into extensors. |