| Goost H et al. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Preliminary experimental results of radiofrequency-cement-augmented and cannulated pedicle screws Journal für Mineralstoffwechsel & Muskuloskelettale Erkrankungen 2011; 18 (Supplementum 1): 23-25 Volltext (PDF) Summary Praxisrelevanz Abbildungen
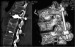
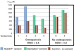
The risk of cut-out of a pedicle screw is high in the presence of osteoporotic bone. In cadaver studies it was found that cement augmentation of pedicle screws markedly increases pullout forces. However, the use of conventional low viscosity vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty cement is associated with the risk of cement extravasation. The risk might be reduced by using high viscosity, radiofrequency-activated bone cement. After performing DEXA scans, six fresh-frozen vertebral bodies of different bone densities were obtained from cadavers. Two pedicle screws (WSI Expertise-Inject, Peter Brehm, Germany) were placed in the pedicles. About 3 ml of radiofrequency-activated, ultra-high viscosity cement (ER2 Bone Cement, DFine Europe GmbH, Germany) was injected through the right pedicle. The left pedicle screw was left uncemented and served as control. Axial pullout tests were performed using a material testing device (Zwick/Roell Zmartpro, Ulm, Germany). The tests revealed that cementaugmented pedicle screws were able to withstand markedly higher pullout forces. Extravasation of cement did not occur. The value of the study is limited by the fact that only six samples were investigated. Further cadaver studies and clinical evaluation will be needed in the future. However, this pilot study showed that combining cannulated pedicle screws with ultra-high viscosity bone cement is a successful approach. Revision due to cut-out and complications secondary to cement extravasation can be reduced by this method. |

Verlag für Medizin und Wirtschaft |
|
||||||||
|
Summary
|
|||||||||
| copyright © 2000–2025 Krause & Pachernegg GmbH | Sitemap | Datenschutz | Impressum | |||||||||
|
|||||||||