Gasser R, Esche G, Gasser S, Holzmann S, Köppel H, Moosbrugger B, Salzer M Indiscriminative Effects of Repaglinide and Other Specific Modulators of Transmembrane KATP-Channel Gating Properties upon Ischaemic/Hypoxic Bovine Coronary Artery Smooth Muscle Relaxation Journal of Clinical and Basic Cardiology 2003; 6 (1-4): 81-85 PDF Summary Overview
| ||||||||||
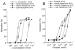
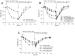
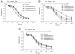
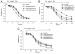
Figure/Graphic 3a-c: Koronararterien - Relaxation A: Relaxation of bovine coronary arteries during hypoxia (open symbols) and its reversibility by reoxygenation; glibenclamide (2 µM) inhibits hypoxic vasodilation; glibenclamide’s intrinsic relaxing activity can be seen in the reoxygenation curve in form of a slight diminution of recovery; B: Dose dependent inhibition by repaglinide of hypoxic vasodilation; C: Dose dependent inhibition by glimepiride of hypoxic vasodilation. The intrinsic relaxing activity of glimepiride can be seen in form of a 17 % initial relaxation of the arteries. This effect was not so pronounced with repaglinide (B). |
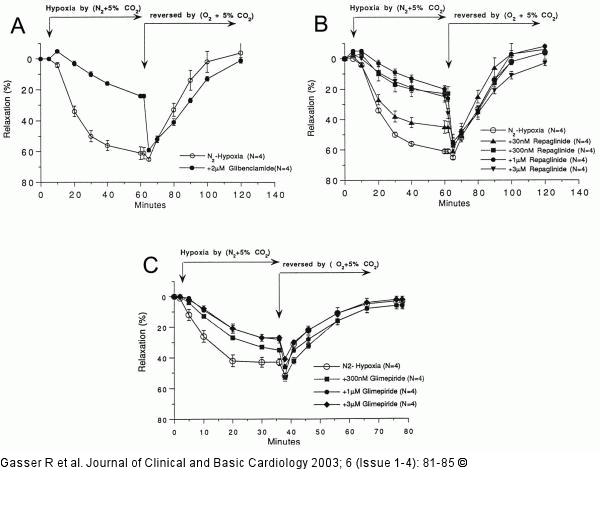
Figure/Graphic 3a-c: Koronararterien - Relaxation
A: Relaxation of bovine coronary arteries during hypoxia (open symbols) and its reversibility by reoxygenation; glibenclamide (2 µM) inhibits hypoxic vasodilation; glibenclamide’s intrinsic relaxing activity can be seen in the reoxygenation curve in form of a slight diminution of recovery; B: Dose dependent inhibition by repaglinide of hypoxic vasodilation; C: Dose dependent inhibition by glimepiride of hypoxic vasodilation. The intrinsic relaxing activity of glimepiride can be seen in form of a 17 % initial relaxation of the arteries. This effect was not so pronounced with repaglinide (B). |