Nicolosi GL Infective Endocarditis: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Issues - Should Transesophageal Echocardiography be Performed in all Patients? - Position Con Journal of Clinical and Basic Cardiology 2001; 4 (2): 161-164 PDF Summary Overview
| ||||||||
Figure/Graphic 4: Endokarditis - Diagnose - TEE Two short axis transoesophageal views, 15 days apart, from an elderly patient with calcific aortic valve and infective endocarditis. In the first examination (top) a vegetation could not be identified since the echogenic nodularities were indistinguishable from fibrocalcific deposits (arrow). In the second examination (bottom) a vegetation was diagnosed on the aortic valve for the evident increase in size of one of the nodularities (arrow) which was still not mobile in real time (see text). A= aortic valve; LA= left atrium |
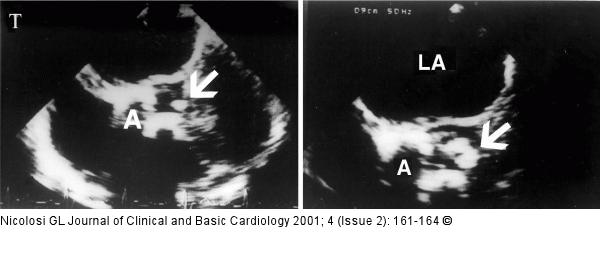
Figure/Graphic 4: Endokarditis - Diagnose - TEE
Two short axis transoesophageal views, 15 days apart, from an elderly patient with calcific aortic valve and infective endocarditis. In the first examination (top) a vegetation could not be identified since the echogenic nodularities were indistinguishable from fibrocalcific deposits (arrow). In the second examination (bottom) a vegetation was diagnosed on the aortic valve for the evident increase in size of one of the nodularities (arrow) which was still not mobile in real time (see text). A= aortic valve; LA= left atrium |




