Pasterkamp C, Falk E Atherosclerotic plaque rupture: an overview Journal of Clinical and Basic Cardiology 2000; 3 (2): 81-86 PDF Summary Overview
| ||
Figure/Graphic 1A-B: Plaqueverteilung und Thrombose Plaque disruption and thrombosis. A. A stenotic coronary plaque containing a huge atheromatous core that is separated from the vascular lumen by a very thin cap of fibrous tissue, ie, a "vulnerable plaque". The fibrous cap is disrupted with superimposed nonocclusive luminal thrombosis. B. Higher magnification of the plaque-thrombus interface. The fibrous cap is very thin (between arrows) and heavily infiltrated by foam cells (fc), probably of macrophage origin. C: contrast medium injected post mortem; T: thrombus |
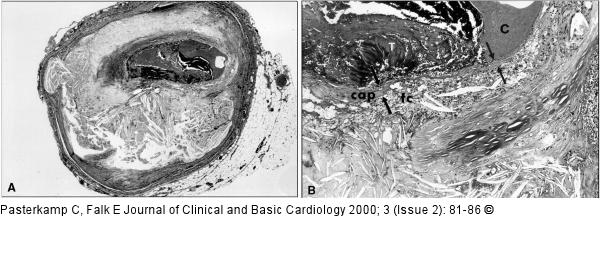
Figure/Graphic 1A-B: Plaqueverteilung und Thrombose
Plaque disruption and thrombosis. A. A stenotic coronary plaque containing a huge atheromatous core that is separated from the vascular lumen by a very thin cap of fibrous tissue, ie, a "vulnerable plaque". The fibrous cap is disrupted with superimposed nonocclusive luminal thrombosis. B. Higher magnification of the plaque-thrombus interface. The fibrous cap is very thin (between arrows) and heavily infiltrated by foam cells (fc), probably of macrophage origin. C: contrast medium injected post mortem; T: thrombus |

