| Gasser R et al. |
|---|
Indiscriminative Effects of Repaglinide and Other Specific Modulators of Transmembrane KATP-Channel Gating Properties upon Ischaemic/Hypoxic Bovine Coronary Artery Smooth Muscle Relaxation
Journal of Clinical and Basic Cardiology 2003; 6 (1-4): 81-85
PDF Summary Figures
| Figure |
|---|
| |
|
|
Koronararterien - Muskelrelaxation
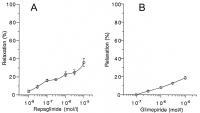
Figure 1a-b: A: Intrinsic relaxing activity of repaglinide in bovine coronary artery in percent of maximal contraction (obtained at the end of each experiment by the addition of 2.66 × 10–4 M papaverine). Strips stabilised in length within 90 min of incubation at about 60 % of maximal shortening; B: Intrinsic relaxing activity of glimepiride at different concentrations like in 1A.
Keywords: coronary artery,
diagram,
Diagramm,
Glatte Muskulatur,
Glimepirid,
glimepiride,
KATP-channel,
KATP-Kanal,
Koronararterie,
Relaxation,
Repaglinid,
Repaglinide,
smooth muscle
|
| |
| |
|
|
Koronararterien - KATP-Kanalöffner-Hemmung
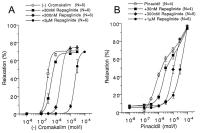
Figure 2a-b: Experiment like in Fig. 1A; repaglinide shows competitive inhibition of specific K channel openers (here shown: pinacidil).
Keywords: coronary artery,
Cromakalim,
Cromakalim,
diagram,
Diagramm,
Hemmung,
inhibition,
KATP-channel,
KATP-Kanal,
Koronararterie,
Pinacidil,
Pinacidil,
Repaglinid,
Repaglinid
|
| |
| |
|
|
Koronararterien - Relaxation
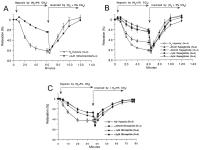
Figure 3a-c: A: Relaxation of bovine coronary arteries during hypoxia (open symbols) and its reversibility by reoxygenation; glibenclamide (2 µM) inhibits hypoxic vasodilation; glibenclamide’s intrinsic relaxing activity can be seen in the reoxygenation curve in form of a slight diminution of recovery; B: Dose dependent inhibition by repaglinide
of hypoxic vasodilation; C: Dose dependent inhibition by glimepiride of hypoxic vasodilation. The intrinsic relaxing activity of glimepiride
can be seen in form of a 17 % initial relaxation of the arteries. This effect was not so pronounced with repaglinide (B).
Keywords: coronary artery,
diagram,
Diagramm,
Glibenclamid,
glibenclamide,
Glimepirid,
glimepiride,
hypoxia,
Hypoxie,
Koronararterie,
Relaxation,
Relaxation,
Repaglinid,
Repaglinide
|
| |
| |
|
|
Koronararterien - Relaxation
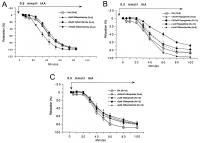
Figure 4a-c: A: Dinitrophenole (1 mM), an uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation invariably leads to vasodilation, the latter is partially inhibited
by glibenclamide in a dose-dependent manner; B: Dose dependent inhibition of DNP-induced vasodilation; note repaglinide’s intrinsic
relaxing activity at higher doses; the inhibition of relaxation is not as pronounced as with glimepiride and glibenclamide; C: Inhibition of DNP induced relaxation is maximal under 3 µM glimepiride; the
effect of a similar dose of glibenclamide is also introduced in this figure in order to demonstrate the approximate equimolar inhibition; glimepiride is a stronger inhibitor of DNP-induced vasorelaxation than glibenclamide.
Keywords: coronary artery,
diagram,
Diagramm,
Gilbenclamid,
Gilbenclamide,
Glimepirid,
glimepiride,
Koronararterie,
realxation,
Relaxation,
Repaglinid,
Repaglinide
|
| |
| |
|
|
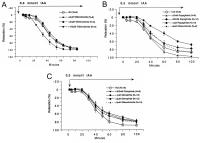
Koronararterien - Relaxation
Figure 5a-c: A: Iodoacetic acid (IAA), an inhibitor of the glycolytic enzyme G3P-dehydrogenase leads to vasodilation; inhibition by glibenclamide,
repaglinide and glimepiride (B) is insignificant; only a dose of 1 µM repaglinide is able to inhibit IAA-induced vasorelaxation after 10 min by 20 %.
Keywords: coronary artery,
diagram,
Diagramm,
Glibenclamid,
glibenclamide,
Glimepirid,
glimepiride,
Koronararterie,
Relaxation,
Relaxation,
Repaglinid,
Repaglinide
|
| |
| |
|
|