| Illmensee K |
|---|
Mammalian Cloning and its Discussion on Applications in Medicine
Journal für Reproduktionsmedizin und Endokrinologie - Journal of Reproductive Medicine and Endocrinology 2007; 4 (1): 6-16
Volltext (PDF) Summary Abbildungen
| Abbildung |
|---|
| |
|
|
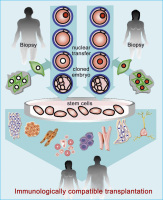
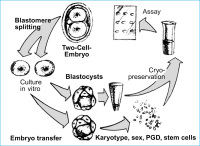
Mammalian embryos
Abbildung 1: Biotechnology on mammalian embryos at various stages of preimplantation development with
multiple applications in reproductive and therapeutic medicine.
Keywords: Andrologie,
Embryo,
Embryologie,
Genetik,
mammalian embryo,
Schema,
scheme
|
| |
| |
|
|
Soamtic cell nuclear transfer
Abbildung 2: Somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) for establishing embryonic stem (ES) cells in therapeutic medicine.
Keywords: Andrologie,
Embryologie,
Genetik,
Schema,
scheme,
SCNT,
somatic cell nuclear transfer,
somatischer Zellkerntransfer
|
| |
| |
|
|
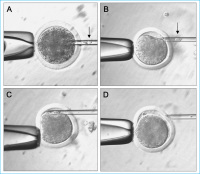
Somatic cell nuclear transfer
Abbildung 3: Interspecies SCNT. (A) Enucleation of bovine oocyte at metaphase II; (B) Selection of
adult human donor cell; (C) Injection of adult human donor cell into the perivitelline space. (D)
Human donor cell attached to the enucleated bovine oocyte.
Keywords: Andrologie,
Embryologie,
Genetik,
SCNT,
soamtischer Zellkern-Transfer,
somatic cell nuclear transfer
|
| |
| |
|
|
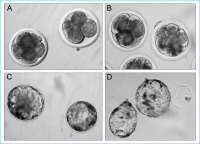
Interspecies-SCNT
Abbildung 4: Interspecies-SCNT preimplantation embryos derived from human granulosa cells fused
with enucleated bovine oocytes. Cleavage embryos (A) and blastocysts (C) derived from SCNT. Parthenogenetically developed cleavage embryos (B) and hatching blastocysts (D) as controls.
Keywords: Andrologie,
Embryologie,
Genetik,
SCNT,
somatic cell nuclear transfer,
somatischer Zellkerntransfer
|
| |
| |
|
|
DNA sequence analysis
Abbildung 5a-b: Human genomic DNA sequence analysis of interspecies-cloned embryo and human adult fibroblast donor cells used for SCNT. Identical
DNA sequence profiles concerning peak positions are detectable for interspecies embryo (A) and human donor cells (B). Some variations in peak
levels result from different sample analysis. Three chromosomal microsatellite probes were used for PCR amplification. FGA (chromosome 4q28),
D21S11 (chromosome 21), D13S317 (chromosome 13q22–31). A standard marker (ABI Applied Biosystem ROX Reference Dye) served as internal
control. For further details see [78].
Keywords: Andrologie,
cell donor,
DNA,
DNA-sequence analysis,
Embryo,
Embryologie,
Genetik,
interspecies-cloned embryo,
Klon
|
| |
| |
|
|
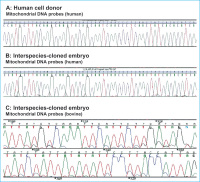
DNA sequence analysis
Abbildung 6a-c: DNA sequence analysis of human and bovine mitochondrial (mt) DNA. From human donor cells and interspeciescloned embryo (blastocyst). For detection of human and bovine mtDNA, species-specific primers were used that amplify parts of the mtD-loop region, respectively. The amplicons were sequenced using internal primers and products separated on an ABI3100.
(A) Human mtD-loop region (position 16191-
16239; GeneBank acc. no. AY275537) that was
amplified from the human donor cells. (B) Human
mtD-loop region obtained from interspecies-cloned
embryo. Both mtDNA sequences show identical
profiles. (C) Bovine mtDNA sequence from interspeciescloned embryo obtained by using bovine mtDNA primers for PCR amplification
of mtD-loop region (position 306 to 359;
GeneBank acc. no. AF499248). For further
details see [78].
Keywords: Andrologie,
bovine embryo,
DNA,
DNA-sequence analysis,
Embryo,
Embryologie,
Genetik,
human embryo
|
| |
| |
|
|
Splitting - Early Embryo
Abbildung 7: Splitting of early embryos (twinning) for various applications in reproductive and therapeutic
medicine.
Keywords: Andrologie,
Embryo,
embryo splitting,
Embryologie,
Genetik,
Schema,
scheme
|
| |
| |
|
|
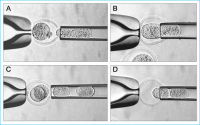
Mouse donor embryo
Abbildung 8: Blastomere biopsy from 2-cell and 4-cell mouse donor embryos (A and C) and blastomere
reinjection into empty zona pellucida recipients (B and D).
Keywords: Andrologie,
balstomere,
Biopsie,
biopsy,
Blastom,
Embryo,
Embryologie,
Genetik
|
| |
| |
|
|
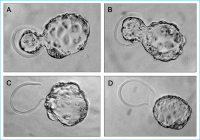
Blastocysts - Mouse embryo
Abbildung 9: Hatching blastocysts derived from mouse embryo splitting at the 2-cell (A and B) and 4-cell
(C and D) stage. Donor blastocysts on the left and recipient blastocysts on the right.
Keywords: Andrologie,
blastozyst,
Blastozyste,
Embryo,
Embryo,
Embryologie,
Genetik
|
| |
| |
|
|