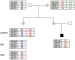
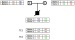
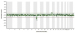
Koehler U, Schoen U, Mayer V, Holinski-Feder E Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis for Monogenic Disorders and Chromosomal Rearrangements – The German Perspective Journal für Reproduktionsmedizin und Endokrinologie - Journal of Reproductive Medicine and Endocrinology 2013; 10 (Sonderheft 1): 38-44 Volltext (PDF) Summary Übersicht
| ||||||||||||||||
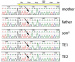
Abbildung 4: PGD for Spinal Muscular Atrophy, SMA PGD for Spinal Muscular Atrophy, SMA. DNA sequence analysis for amplification products of exon 7 in mother, father, affected son and two trophectoderm biopsies (TE1, TE2). The mother and father are heterozygous for the nucleotide (C or T) in exon 7 corresponding to the presence of gene copies of SMN1 and SMN2. The son shows only the T-nucleotide of the SMN2 gene and thus carries a homozygous deletion in SMN1. Both TE samples show both nucleotides at this base position, indicating that the blastocysts are either wild type or heterozygous carriers of the deletion. |
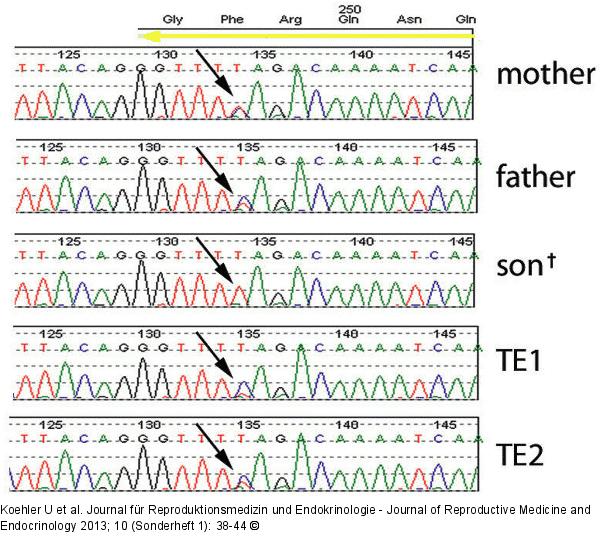
Abbildung 4: PGD for Spinal Muscular Atrophy, SMA
PGD for Spinal Muscular Atrophy, SMA. DNA sequence analysis for amplification products of exon 7 in mother, father, affected son and two trophectoderm biopsies (TE1, TE2). The mother and father are heterozygous for the nucleotide (C or T) in exon 7 corresponding to the presence of gene copies of SMN1 and SMN2. The son shows only the T-nucleotide of the SMN2 gene and thus carries a homozygous deletion in SMN1. Both TE samples show both nucleotides at this base position, indicating that the blastocysts are either wild type or heterozygous carriers of the deletion. |