Ising H, Babisch W, Günther T Work noise as a risk factor in myocardial infarction Journal of Clinical and Basic Cardiology 1999; 2 (1): 64-68 PDF Summary Overview
| ||||||
Figure/Graphic 3: Lärmwirkung Relative risk (RR) of MI in men (and 95 % confidence intervals) by work noise category. Work noise was assessed by subjective loudness comparison with typical noise sources (1+2: refrigerator + typewriter, 3: electric lawn-mower, 4: electric drill, 5: road drill). Relative risk of MI (ICD 410) was adjusted for covariates (smoking, body mass index, age, social class, education, marital status, shift work, housing area) using logistic analysis. |
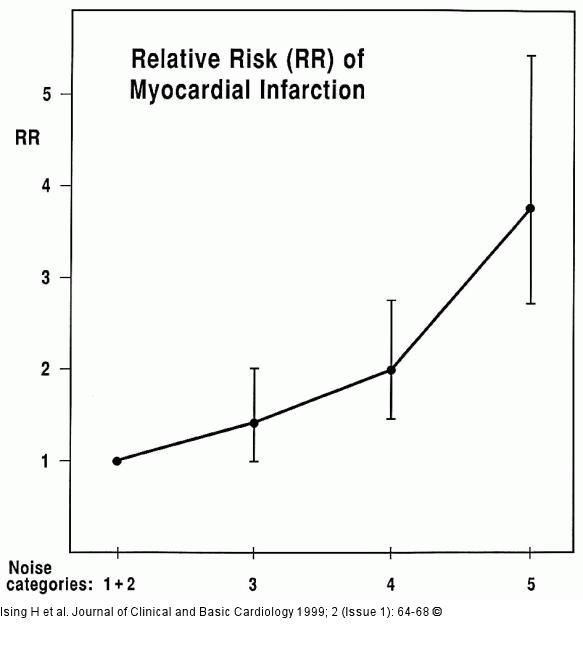
Figure/Graphic 3: Lärmwirkung
Relative risk (RR) of MI in men (and 95 % confidence intervals) by work noise category. Work noise was assessed by subjective loudness comparison with typical noise sources (1+2: refrigerator + typewriter, 3: electric lawn-mower, 4: electric drill, 5: road drill). Relative risk of MI (ICD 410) was adjusted for covariates (smoking, body mass index, age, social class, education, marital status, shift work, housing area) using logistic analysis. |