Zehetgruber M, Berger R, Christ G, Huber K, Kostner K, Mundigler G, Neunteufl T Basal and stimulated release of long-acting EDRF by bovine pulmonary arteries Journal of Clinical and Basic Cardiology 1999; 2 (1): 117-119 PDF Summary Overview
| ||||
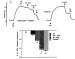
Figure/Graphic 2: Pulmonalarterie - Relaxation Relaxation of bovine pulmonary arteries under stimulated conditions. A: Representative tracing. In the upper panel significant relaxation was induced by perfusing the detector with effluent of an endothelium intact pulmonary artery (generator) which was collected and stored prior to perfusion for five minutes (CE). Addition of acetylcholine (ACh 10-6 M) to the perfusion medium of the generator (CE-ACh) augmented relaxation. Following direct superfusion (G-ACh), relaxation was more pronounced. In control experiments (lower panel) only direct superfusion was performed; W = wash. B: Average relaxation. |

Figure/Graphic 2: Pulmonalarterie - Relaxation
Relaxation of bovine pulmonary arteries under stimulated conditions. A: Representative tracing. In the upper panel significant relaxation was induced by perfusing the detector with effluent of an endothelium intact pulmonary artery (generator) which was collected and stored prior to perfusion for five minutes (CE). Addition of acetylcholine (ACh 10-6 M) to the perfusion medium of the generator (CE-ACh) augmented relaxation. Following direct superfusion (G-ACh), relaxation was more pronounced. In control experiments (lower panel) only direct superfusion was performed; W = wash. B: Average relaxation. |