Dia-Präsentation von Merck Gesellschaft mbH. Micardis(R) - MicardisPlus(R) - Hypertonie (38 Abbildungen) Übersicht Gesamtpräsentation zum Download (rechte Maustaste und "Ziel speichern unter..." klicken)
| ||||||||||||||||||
Abbildung 26: Behandlungsschema - ESH-ESC ESH–ESCguidelines also emphasize the need to consider ancillary risk factors when setting treatment goals.1 Shown in this table is the blood pressure at diagnosis. Risk factors include diabetes, smoking, abdominal obesity and target-organ damage (such as LVH, microalbuminuria or increased serum creatinine), as well as associated clinical conditions such as cardiovascular or renal disease. Patients at high risk or very high risk should have their blood pressure treated if it is above 130/85 mmHg. Patients with blood pressure that is consistently >140/90 mmHg should usually have it treated, regardless of the presence of other risk factors. 1. 2003 European Society of Hypertension – European Society of Cardiology guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. J Hypertens 2003; 21: 1011–1053. |
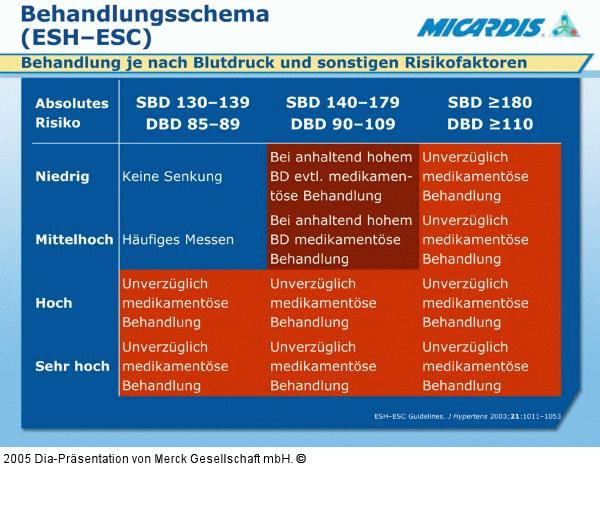
Abbildung 26: Behandlungsschema - ESH-ESC
ESH–ESCguidelines also emphasize the need to consider ancillary risk factors when setting treatment goals.1 Shown in this table is the blood pressure at diagnosis. Risk factors include diabetes, smoking, abdominal obesity and target-organ damage (such as LVH, microalbuminuria or increased serum creatinine), as well as associated clinical conditions such as cardiovascular or renal disease. Patients at high risk or very high risk should have their blood pressure treated if it is above 130/85 mmHg. Patients with blood pressure that is consistently >140/90 mmHg should usually have it treated, regardless of the presence of other risk factors. 1. 2003 European Society of Hypertension – European Society of Cardiology guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. J Hypertens 2003; 21: 1011–1053. |







