Dia-Präsentation von Merck Gesellschaft mbH. Micardis(R) - MicardisPlus(R) - Hypertonie (38 Abbildungen) Übersicht Gesamtpräsentation zum Download (rechte Maustaste und "Ziel speichern unter..." klicken)
| ||||||||||||||||||
Abbildung 23: Blutdrucksenkung - Vorteile Intensive antihypertensive treatment (i.e. with a target DBP ≤85 mmHg) can significantly reduce the risk of a major cardiovascular event compared with less intensive treatment (target DBP ≤90 mmHg). The data shown in this slide are from the Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) study of 18,790 hypertensives treated for an average 3.8 years.1 Benefits were greatest in diabetics (relative risk = 0.53 for cardiovascular events).1 In non-smokers, there was reduced risk in many important patient groups, including those with a global risk considered to be high or very high.1 In smokers, more intensive DBP lowering was associated with increased risk of all types of cardiovascular event.1 1. Zanchetti A, et al. Benefits and risks of more intensive blood pressure lowering in hypertensive patients of the HOT study with different risk profiles: does a J-shaped curve exist in smokers? J Hypertens 2003; 21: 797–804. |
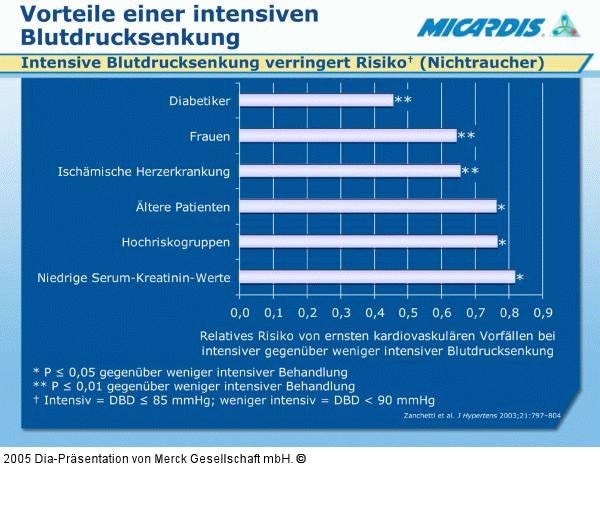
Abbildung 23: Blutdrucksenkung - Vorteile
Intensive antihypertensive treatment (i.e. with a target DBP ≤85 mmHg) can significantly reduce the risk of a major cardiovascular event compared with less intensive treatment (target DBP ≤90 mmHg). The data shown in this slide are from the Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) study of 18,790 hypertensives treated for an average 3.8 years.1 Benefits were greatest in diabetics (relative risk = 0.53 for cardiovascular events).1 In non-smokers, there was reduced risk in many important patient groups, including those with a global risk considered to be high or very high.1 In smokers, more intensive DBP lowering was associated with increased risk of all types of cardiovascular event.1 1. Zanchetti A, et al. Benefits and risks of more intensive blood pressure lowering in hypertensive patients of the HOT study with different risk profiles: does a J-shaped curve exist in smokers? J Hypertens 2003; 21: 797–804. |







