| Zweiker D et al. | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Die Defibrillatorweste im Laufe der Jahre // The wearable cardioverter defibrillator over the years Journal für Kardiologie - Austrian Journal of Cardiology 2025; 32 (5-6): 92-96 Volltext (PDF) Summary Abbildungen
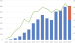
Keywords: Cardioverter-Defibrillator, Defibrillatorweste, Herzinsuffizienz, neurohumorale Therapie, cardioverter defibrillator, heart failure, neurohumoral therapy, wearable cardioverter defibrillator Introduction: The wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) is an alternative to conventional implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) therapy to reduce the risk of sudden cardiac death in patients with cardiac disease temporary contraindication to ICD. While the WCD is indicated in certain situations according to current guidelines, its use in daily clinical practice is unclear. Methods: We performed an analysis of all first WCD prescriptions in Austria and compared indications, outcome and definite treatments at three timepoints: 2010–2015, 2016–2020 and 2021–2024. Results: Between July 2010 and July 2024 the WCD was prescribed in 4258 patients in 78 centres, with an increasing number of prescriptions within the last years (n = 1.982 in 2021–2024 vs. 419 in 2010–2015). Ischemic cardiomyopathy was the indication in about one third of patients (31.7–34.0%, p = 0.331) and the rate of appropriate shock (1.2–2.1%, p = 0.264) and inappropriate shock (0.0–0.7%, p = 0.224) was similar throughout all timepoints. In the last years, the rate of definite ICD implantations after WCD prescription decreased (2010–2015: 38.9% vs. 2021–2024: 26.9%, p < 0.001) and the proportion of patients with recovery of left ventricular dysfunction increased (23.2% vs. 34.3%, p < 0.001). Discussion: For 25 years, the WCD is an established option for bringing therapy in patients with increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias. A reduced rate of ICD implantations and increased rate of recovered left ventricular dysfunction after WCD use in the last years may be a result of advances in neurohumoral therapy in patients with heart failure and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction.
Kurzfassung: Einleitung: Für Patienten mit Herzerkrankung und temporärer Kontraindikation für einen implantierbaren Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD) besteht die Möglichkeit der Defibrillatorweste („Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillator“, WCD) zur Reduktion des plötzlichen Herztods. Während der WCD laut aktueller Leitlinien für spezielle Indikationen empfohlen wird, ist die Verwendung in der täglichen Praxis oft unklar. |

Verlag für Medizin und Wirtschaft |
|
||||||||
|
Summary
|
|||||||||
| copyright © 2000–2026 Krause & Pachernegg GmbH | Sitemap | Datenschutz | Impressum | |||||||||
|
|||||||||