| Nitschke T et al. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The CPET-HFpEF Score: a noninvasive test for the diagnosis of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction // Der CPET-HFpEF-Score: ein nichtinvasiver Test zur Diagnose der Herzinsuffizienz mit erhaltener Ejektionsfraktion Journal für Kardiologie - Austrian Journal of Cardiology 2025; 32 (9-10): 200-207 Volltext (PDF) Summary Abbildungen
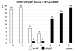
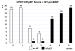
Keywords: CPET, Herzinsuffizienz, HFpEF, Spiroergometrie, cardiopulmonary exercise testing, heart failure Introduction: The diagnosis of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is still challenging, with the gold standard being invasive testing. For noninvasive diagnosis two multiparameter risk scores exist, the HFA-PEFF and the H2FPEF-scoring systems. Both integrate morphological evidence of structural heart disease from echocardiography, historical features or laboratory assessment of natriuretic peptides. However, there is still a gap in accuracy when these results are inconclusive. Here, we present a noninvasive test for the diagnosis of HFpEF that is based on cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) parameters. Methods / results: CPET is the gold standard for identifying the cause of unexplained dyspnoea and/or exercise intolerance, the main symptoms of heart failure. CPET was performed with a total of 100 patients, 50 with HFpEF estimated by the HFA-PEFF score of 6 and 50 patients without a diagnosis of heart failure. For our score we only used parameters with the highest diagnostic accuracy for diagnosing heart failure, which was estimated via an unpaired t-test. Thresholds for the diagnosis of HFpEF were estimated via logistic regression analysis and adjusted by the known threshold, described in the literature. The accuracy of various combinations of parameters for the score was tested via ROC-curve-analysis. By combining five parameters of the CPET (VO2peak indexed by body weight, VE/VCO2 slope, oxygen uptake efficiency slope [OUES], VO2/WR slope and the increase in PetCO2 during exercise [PetCO2 delta]) we obtained a sensitivity of 91% and a specificity of 96% for the diagnosis of HFpEF. By adding the NT-proBNP value, the sensitivity improved to 100% and the specificity remained at 96%. Conclusion: The CPET-HFpEF score allows the confirmation of the diagnosis of HFpEF in patients with exercise intolerance and dyspnoea with one comprehensive whole-body testing technique. In combination with the determination of NT-proBNP, the high diagnostic accuracy can be further improved.
Kurzfassung: Einleitung: Die Diagnose der Herzinsuffizienz mit erhaltener Ejektionsfraktion (HFpEF) ist nach wie vor schwierig, der Goldstandard ist eine invasive Rechtsherzkatheteruntersuchung. Für die nichtinvasive Diagnose gibt es zwei Multiparameter-Risikoscores, das HFA-PEFF- und das H2FPEF-Scoring-System. Beide integrieren morphologische Anzeichen einer strukturellen Herzerkrankung aus der Echokardiographie, Daten der Krankengeschichte und der HFA-PEFF-Score die Bestimmung von natriuretischen Peptiden. Es gibt jedoch immer noch eine Lücke in der Genauigkeit, wenn der Score nicht eindeutig ist. Wir haben einen nicht-invasiven Test zur Diagnose von HFpEF entwickelt, der Parameter der Spiroergometrie (CPET) verwendet. |

Verlag für Medizin und Wirtschaft |
|
||||||||
|
Summary
|
|||||||||
| copyright © 2000–2026 Krause & Pachernegg GmbH | Sitemap | Datenschutz | Impressum | |||||||||
|
|||||||||