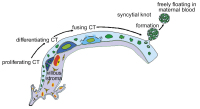
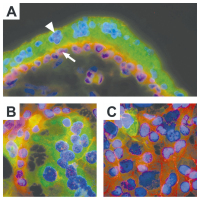
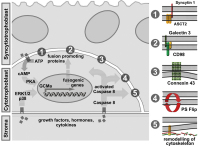
Trophoblast fusion
Abbildung 3: Illustration of factors involved in trophoblast fusion. Environmentally derived growthfactors, hormones and cytokines bind to their cognate receptors at the plasma membrane ofcytotrophoblasts. Activation of either protein kinase A (PKA) or MAP kinases ERK1/2 and p38leads to increased protein expression of the transcription factor GCMa, which in turn drivestranscription of fusogenic genes. Several structural and membrane proteins were suggested topromote trophoblast fusion, including syncytin 1 and its receptor ASCT2 (1), CD98 and its receptorgalectin 3 (2) as well as connexin 43 (3). Beside activation of PKA or MAP kinase pathways,cytokines induce conversion of pro-caspase 8 into active caspase 8. Once activated, caspase 8can mediate inactivation of “flippases” and/or activation of "floppases" to trigger phosphatidyl-serine externalisation (PS flip) (4). Additionally, caspase 8 triggers remodelling of the sub-mem-branous cytoskeleton by degrading structural proteins such as α-fodrin (5).
Keywords:
Throphoblast,
trophoblast fusion