Gauster M, Huppertz B Fusion of Cytothrophoblast with Syncytiotrophoblast in the Human Placenta: Factors Involved in Syncytialization Journal für Reproduktionsmedizin und Endokrinologie - Journal of Reproductive Medicine and Endocrinology 2008; 5 (2): 76-82 Volltext (PDF) Summary Übersicht
| ||||||
Abbildung 1: Trophoblast Schematic representation of trophoblast differentiation within the villous trophoblast.Derived from trophoblast progenitor cells daughter cells start to differentiate and finally fusewith the overlying syncytiotrophoblast. Nuclei that have become an integrative part of the syn-cytiotrophoblast change their morphology and display chromatin condensation. Finally lateapoptotic syncytial nuclei are packed into syncytial knots and are released into the maternalblood stream. The arrows follow the route of cell types and nuclear changes during trophoblastdifferentiation. |
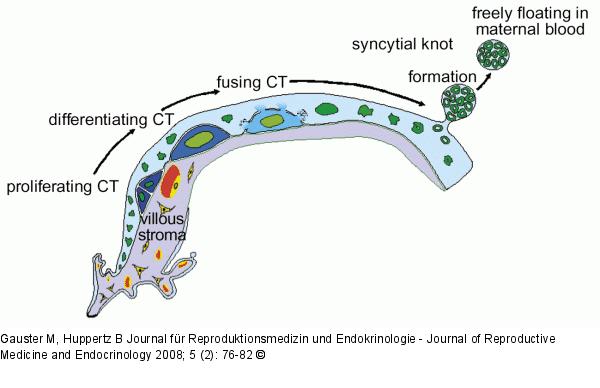
Abbildung 1: Trophoblast
Schematic representation of trophoblast differentiation within the villous trophoblast.Derived from trophoblast progenitor cells daughter cells start to differentiate and finally fusewith the overlying syncytiotrophoblast. Nuclei that have become an integrative part of the syn-cytiotrophoblast change their morphology and display chromatin condensation. Finally lateapoptotic syncytial nuclei are packed into syncytial knots and are released into the maternalblood stream. The arrows follow the route of cell types and nuclear changes during trophoblastdifferentiation. |