McGuigan JAS, Elder HY, GŁnzel D, Schlue W-R Magnesium Homeostasis in Heart: A Critical Reappraisal Journal of Clinical and Basic Cardiology 2002; 5 (1): 5-22 PDF Summary Overview
| ||||||||||||
Figure/Graphic 1: Ionen - Magnesium 1. Chemical potential for the ionic gradients. The organic anions, malate, citrate, lactate and pyruvate are labelled M2-, Ci2-, L- and Py- respectively. This illustrates that due to the difference in the chemical potential between that required to extrude Mg2+ and that of Cl- and K+ these ions a priori would be unlikely to form a symport with Mg2+ |
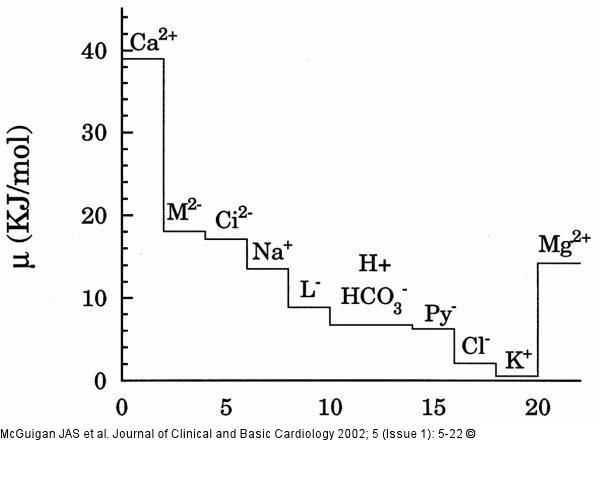
Figure/Graphic 1: Ionen - Magnesium
1. Chemical potential for the ionic gradients. The organic anions, malate, citrate, lactate and pyruvate are labelled M2-, Ci2-, L- and Py- respectively. This illustrates that due to the difference in the chemical potential between that required to extrude Mg2+ and that of Cl- and K+ these ions a priori would be unlikely to form a symport with Mg2+ |