McGuigan JAS, Elder HY, GŁnzel D, Schlue W-R Magnesium Homeostasis in Heart: A Critical Reappraisal Journal of Clinical and Basic Cardiology 2002; 5 (1): 5-22 PDF Summary Overview
| ||||||||||||
Figure/Graphic 2: Magnesiumefflux - Atrium Preliminary measurements of Mg2+ efflux from cultured atrial cells. The background solution contained in mmol/l: Na+, 155; K+, 5; Ca2+, 0.9; and no added Mg2+, buffered to pH 7.4 with 5 mmol/l HEPES. After 6 minutes the cell pellet was added to the background solution. Because of contamination this increased the [Mg2+] from around 15 micromol/l to 60 micromol/l. Addition of adrenaline caused an efflux of Mg2+ from the cells. The electrode did not react to 30 micromol/l adrenaline |
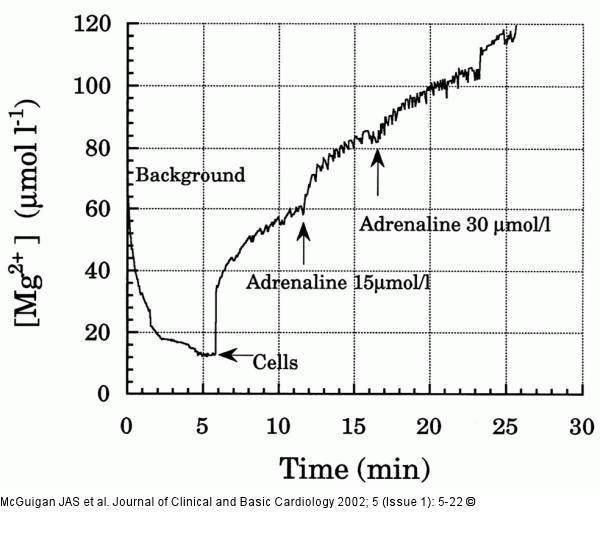
Figure/Graphic 2: Magnesiumefflux - Atrium
Preliminary measurements of Mg2+ efflux from cultured atrial cells. The background solution contained in mmol/l: Na+, 155; K+, 5; Ca2+, 0.9; and no added Mg2+, buffered to pH 7.4 with 5 mmol/l HEPES. After 6 minutes the cell pellet was added to the background solution. Because of contamination this increased the [Mg2+] from around 15 micromol/l to 60 micromol/l. Addition of adrenaline caused an efflux of Mg2+ from the cells. The electrode did not react to 30 micromol/l adrenaline |