Montag M, Toth B, Strowitzki T New Laboratory Techniques in Reproductive Medicine Journal für Reproduktionsmedizin und Endokrinologie - Journal of Reproductive Medicine and Endocrinology 2013; 10 (Sonderheft 1): 33-37 Volltext (PDF) Summary Übersicht
| ||||
Abbildung 1: Result of an array-CGH analysis This example shows the result of an array-CGH analysis of the 1st polar body from an oocyte taken from a patient with a maternal reciprocal translocation 46,XX,t(5;8)(q22;p11.2). The possibility to detect numerical (loss of a chromatid 15 and 16) and structural chromosomal aberrations (gain of a chromatid 8p and loss of a chromatid 5q) by array-CGH is obvious. Reprinted in part with permission from [Montag et al., J Reproduktionsmed Endokrinol 2010; 6: 498–502]. |
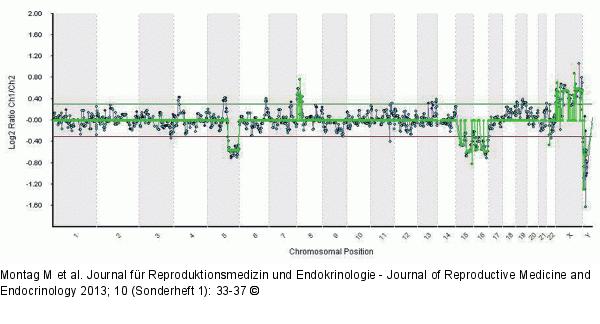
Abbildung 1: Result of an array-CGH analysis
This example shows the result of an array-CGH analysis of the 1st polar body from an oocyte taken from a patient with a maternal reciprocal translocation 46,XX,t(5;8)(q22;p11.2). The possibility to detect numerical (loss of a chromatid 15 and 16) and structural chromosomal aberrations (gain of a chromatid 8p and loss of a chromatid 5q) by array-CGH is obvious. Reprinted in part with permission from [Montag et al., J Reproduktionsmed Endokrinol 2010; 6: 498–502]. |


