Kopp AF, Claussen CD, Heuschmid M, Kuettner A, Schroeder S New Developments in Cardiac Imaging: The Role of MDCT Journal of Clinical and Basic Cardiology 2001; 4 (4): 253-260 PDF Summary Overview
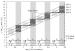
| ||||||||||||
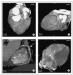
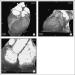
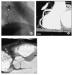
Figure/Graphic 5a-c: MDCT-Computertomographie Male patient, age 62, known 2-vessel-disease, s/p PTCA of proximal LAD. Patient presented with recurrent chest–pain and angina. (a) RAO-projection of conventional angiogram reveals high grade stenosis of descending RCA. (b) LAO projection of RCA by MDCT (collimation 4 x 1 mm, pitch 1.5, 120 cc Imeron(R) 400) depicts the proximal lesion as well as wall changes throughout the vessel. (c) Axial CT image of the mid-lesion region: the degree of stenosis is estimated to 80 % (arrow). |
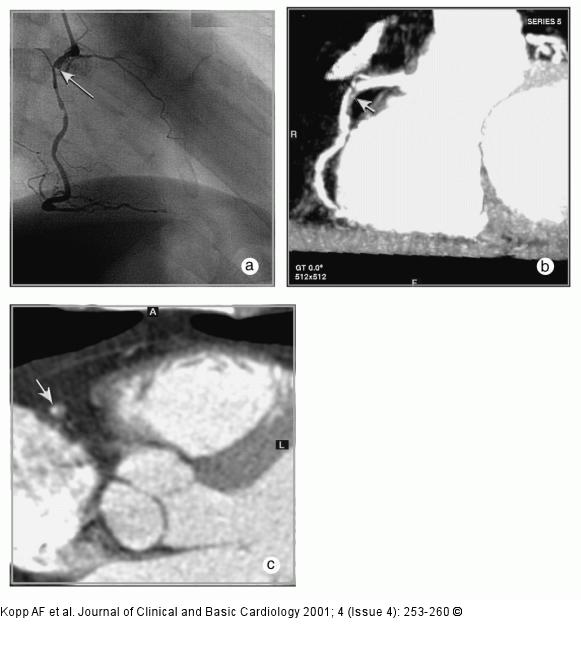
Figure/Graphic 5a-c: MDCT-Computertomographie
Male patient, age 62, known 2-vessel-disease, s/p PTCA of proximal LAD. Patient presented with recurrent chest–pain and angina. (a) RAO-projection of conventional angiogram reveals high grade stenosis of descending RCA. (b) LAO projection of RCA by MDCT (collimation 4 x 1 mm, pitch 1.5, 120 cc Imeron(R) 400) depicts the proximal lesion as well as wall changes throughout the vessel. (c) Axial CT image of the mid-lesion region: the degree of stenosis is estimated to 80 % (arrow). |