Kopp AF, Claussen CD, Heuschmid M, Kuettner A, Schroeder S New Developments in Cardiac Imaging: The Role of MDCT Journal of Clinical and Basic Cardiology 2001; 4 (4): 253-260 PDF Summary Overview
| ||||||||||||
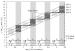
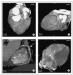
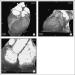
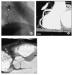
Figure/Graphic 6a-h: MDCT-Computertomographie Male patient, age 55, with "situs inversus" and 2-vessel-disease, s/p PTCA of proximal RCA and prox. LAD, a 60 % lesion of distal RCA was left untreated. (a) Anterior view (volume rendering mode) of thorax with ventral thorax wall cut away depicts situs inversus. (b) RAO projection of RCX and prominent marginal branch in volume rendering mode. No highgrade lesion can be readily appreciated. (c) MIP of RCX clearly shows a lesion (arrow). The degree of stenosis is estimated at 70 %. (d) RAO cranial view of proximal LAD in volume rendering mode. The high-grade lesion was not clearly delineated in this view. (e) MIP-image clearly depicted the lesion of the proximal LAD. (f) MIP of RCA in "left posterior oblique"-projection. The arrow depicts the distal RCA lesion. The black arrow shows the area of the former dilatation, no restenosis present. (g) LAO cranial view of LAD and RCX with conventional angio. The arrows depict the lesions in each of the vessels. (h) RAO view of RCA by conventional angiography. Note the progress of the former 60 % lesion to a high-grade lesion and the absent restenosis of the proximal RCA. |
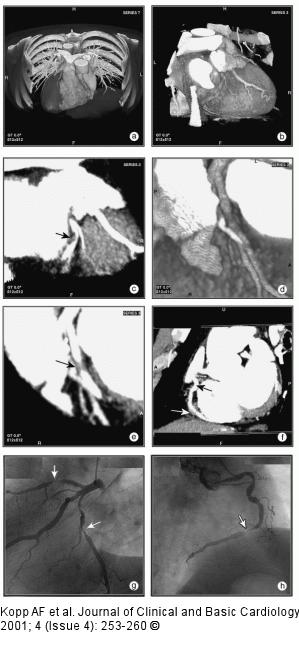
Figure/Graphic 6a-h: MDCT-Computertomographie
Male patient, age 55, with "situs inversus" and 2-vessel-disease, s/p PTCA of proximal RCA and prox. LAD, a 60 % lesion of distal RCA was left untreated. (a) Anterior view (volume rendering mode) of thorax with ventral thorax wall cut away depicts situs inversus. (b) RAO projection of RCX and prominent marginal branch in volume rendering mode. No highgrade lesion can be readily appreciated. (c) MIP of RCX clearly shows a lesion (arrow). The degree of stenosis is estimated at 70 %. (d) RAO cranial view of proximal LAD in volume rendering mode. The high-grade lesion was not clearly delineated in this view. (e) MIP-image clearly depicted the lesion of the proximal LAD. (f) MIP of RCA in "left posterior oblique"-projection. The arrow depicts the distal RCA lesion. The black arrow shows the area of the former dilatation, no restenosis present. (g) LAO cranial view of LAD and RCX with conventional angio. The arrows depict the lesions in each of the vessels. (h) RAO view of RCA by conventional angiography. Note the progress of the former 60 % lesion to a high-grade lesion and the absent restenosis of the proximal RCA. |