Wicher C, Biewald G-A Left-ventricular dysfunction, heart vagus influences and angiotensin II effects after doxorubicin perfusion in isolated rat hearts Journal of Clinical and Basic Cardiology 1999; 2 (2): 259-266 PDF Summary Overview
| ||||||||||||||||
Figure/Graphic 6A-D: Doxorubicin - Angiotensin-II-Modulation Time courses of heart rate (HR, A), SαT time (B), systolic pressure PS (C) and time constant of contraction τC (D) and changes in above parameters during vagus stimulation (right N. vagus, 10 Hz, 10 V), recorded in an isolated rat heart (modified Langendorff preparation) before and during doxorubicin (DXR) perfusion (20 micromol/L) and after addition of angiotensin II (AII, 1 micro mol/L). AII was added 20 min after DXR application to Tyrode solution. Small vertical arrows which originate from the curves, show changes in the parameters mentioned above, caused by vagus stimulation. Note, that vagus effects were progressively reduced during DXR perfusion. Addition of AII caused positive chronotropic and inotropic effects for a short time. Additionally, AII addition reduced vagus stimulation effects regarding above parameters (especially HR and PS). At the end of experiment, all vagus effects were nearly completely disappeared. |
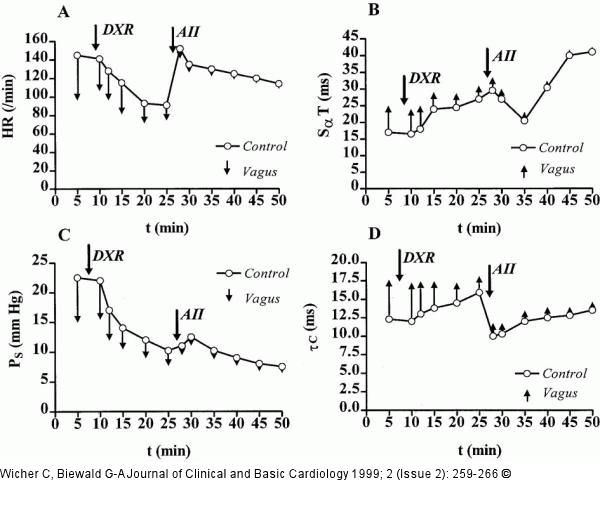
Figure/Graphic 6A-D: Doxorubicin - Angiotensin-II-Modulation
Time courses of heart rate (HR, A), SαT time (B), systolic pressure PS (C) and time constant of contraction τC (D) and changes in above parameters during vagus stimulation (right N. vagus, 10 Hz, 10 V), recorded in an isolated rat heart (modified Langendorff preparation) before and during doxorubicin (DXR) perfusion (20 micromol/L) and after addition of angiotensin II (AII, 1 micro mol/L). AII was added 20 min after DXR application to Tyrode solution. Small vertical arrows which originate from the curves, show changes in the parameters mentioned above, caused by vagus stimulation. Note, that vagus effects were progressively reduced during DXR perfusion. Addition of AII caused positive chronotropic and inotropic effects for a short time. Additionally, AII addition reduced vagus stimulation effects regarding above parameters (especially HR and PS). At the end of experiment, all vagus effects were nearly completely disappeared. |