| Hosmann A et al. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
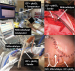
Die zerebrale Mikrodialyse – der Blick hinter die Blut-Hirn-Schranke direkt am neurochirurgischen Intensivbett bei Patienten nach aneurysmatischer Subarachnoidalblutung // Cerebral microdialysis Journal für Neurologie, Neurochirurgie und Psychiatrie 2022; 23 (1): 10-15 Volltext (PDF) Summary Praxisrelevanz Abbildungen
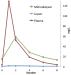
Keywords: Ischämie, Mikrodialyse, multimodales Neuromonitoring, Neurochirurgie, Pharmakokinetik, Subarachnoidalblutung, ischemia, microdialysis, multimodality neuromonitoring, neurosurgery, pharmacokinetics, subarachnoid hemorrhage Cerebral microdialysis is a minimally invasive procedure to determine virtually any compound in-vivo behind the blood-brain barrier. A thin microcatheter is placed directly in the brain parenchyma, which communicates with the cerebral interstitial fluid via a semipermeable membrane in similar to a blood capillary. The microdialysis technique allows to collect any extracellular low molecular weight substance, including metabolites, prognostic factors and administered drugs beyond the blood-brain barrier. At the neurosurgical intensive care unit the microdialysis procedure is primarily used in patients suffering from severe subarachnoid hemorrhage. In clinical routine, the metabolites glucose, lactate, pyruvate, glutamate, and glycerol are determined within the brain parenchyma. In the sedated and mechanically ventilated intensive care patient, these metabolites allow an early detection of secondary ischemic events and thus providing an adequate time window to initiate therapeutic interventions. Furthermore, the individual metabolic response to targeted therapy can be evaluated and therapeutic strategies readapted on an individual basis to improve cerebral metabolism. Additionally, the routinely determined metabolites are prognostic markers for the patients’ functional outcome. Novel cerebral metabolites might provide new insights into pathophysiological processes following cerebral diseases. Using the microdialysis technique pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of drugs can be determined in vivo directly within the brain parenchyma. Thereby, the unbound interstitial – and thus pharmacologically active – drug concentration beyond the blood-brain barrier is measured. In conclusion, cerebral microdialysis is an excellent technique for early detection of cerebral ischemia and individual adaptation of targeted therapies according to the current metabolic situation. As a unique research tool it provides insight into cerebral pharmacokinetic of drugs and might enhance our understanding of ongoing pathophysiological processes beyond the blood-brain barrier.
Kurzfassung: Die zerebrale Mikrodialyse ist ein
minimal-invasives Verfahren, um direkt am Patientenbett Substanzen im Hirnparenchym innerhalb der
Blut-Hirn-Schranke zu bestimmen. Hierfür wird ein
dünner Katheter im Gehirnparenchym platziert, welcher
über eine semipermeable Membran wie eine
Blutkapillare mit der umliegenden interstitiellen
Flüssigkeit kommuniziert. Mit Hilfe dieses Verfahrens
können jegliche extrazelluläre niedermolekulare
Substanzen einschließlich Metaboliten, Prognosefaktoren
und verabreichte Arzneimittel hinter der
Blut-Hirn-Schranke bestimmt werden. |

Verlag für Medizin und Wirtschaft |
|
||||||||
|
Summary
|
|||||||||
| copyright © 2000–2026 Krause & Pachernegg GmbH | Sitemap | Datenschutz | Impressum | |||||||||
|
|||||||||